
Corrosion resistance for screws and other fasteners
Corrosion resistance for screws and other fasteners
Galvanic coatings for screws and fasteners
Electroplating, also known as galvanic coating, is a type of surface treatment used to improve the corrosion resistance of screws and other fasteners.
In electroplating, electricity is passed through an electrolytic bath. The metal to be applied (e.g. zinc or nickel) is located at the positive pole (anode) and the object to be coated at the negative pole (cathode). The electric current removes metal ions from the consumable electrode and deposits them on the product by reduction. In this way, the object to be plated is evenly coated on all sides with copper or another metal. The longer the object is in the bath and the higher the electric current, the stronger the metal layer (e.g. zinc layer) becomes.
Galvanic coatings offer several advantages. They improve corrosion resistance, can extend the life of fasteners and can also improve the appearance of parts. In addition, they can help to improve the frictional properties of the parts, which can improve their performance.
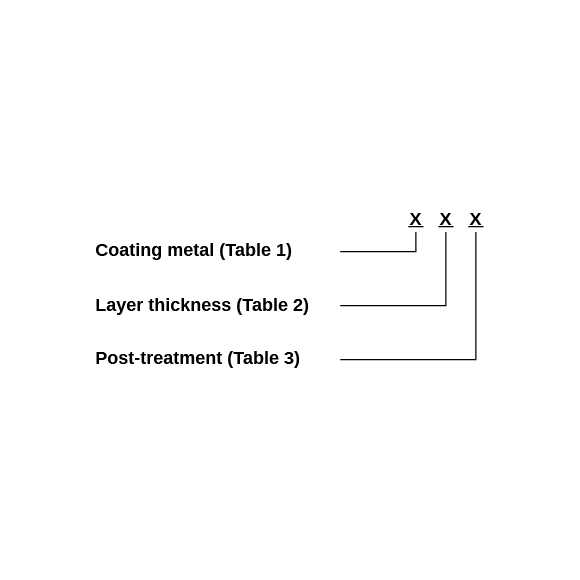
Here you can see an example of shortcuts for electroplated coatings using an M8 x 25 - A2L screw.
| Coating metals (Table 1) | ||
| Coating metal | Identification letter |
|
| Abbreviation | Element | |
| Zn | Zinc | A |
| Cd* | Cadmium | B |
| Cu | Copper | C |
| CuZn | Copper-Zinc | D |
| Ni b* | Nickel | E |
| Ni b Cr r* | Nickel-Chrome | F |
| CuNi b* | Copper-Nickel | G |
| CuNi b Cr r* | Copper-Nickel-Chrome | H |
| Sn | Tin | J |
| CuSn | Copper-Tin | K |
| Ag | Silver | L |
| CuAg | Copper-Silver | N |
| ZnNi | Zinc-Nickel | P |
| ZnCo | Zinc-Cobalt | Q |
| ZnFe | Zinc Iron | R |
The use of cadmium is restricted in certain countries *The ISO classification code is in ISO 1456 |
||
| Layer thickness (Table 2) | ||
| Layer thickness (µm) | Code |
|
| One coating metal | Two coating metals* | |
| no layer thickness specified | - | 0 |
| 3 | - | 1 |
| 5 | 2 + 3 | 2 |
| 8 | 3 + 5 | 3 |
| 10 | 4 + 6 | 9 |
| 12 | 4 + 8 | 4 |
| 15 | 5 + 10 | 5 |
| 20 | 8 + 12 | 6 |
| 25 | 10 + 15 | 7 |
| 30 | 12 + 18 | 8 |
| *The thicknesses specified for the first and second coating metals apply to all combinations of coatings with the exception that chromium is the top layer, which always has a thickness of 0.3 µm. | ||
| Post-treatment and passivation by chromating (Table 3) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Gloss level | Passivation by chromating* Self color |
Identification letter |
| matt | No color | A |
| matt | bluish to bluish iridescent² | B |
| matt | yellowish shimmering to yellow-brown, iridescent | C |
| matt | olive green to olive brown | D |
| plain | No color | E |
| plain | bluish to bluish iridescent² | F |
| plain | yellowish shimmering to yellow-brown, iridescent | G |
| plain | olive green to olive brown | H |
| shiny | No color | J |
| shiny | bluish to bluish iridescent² | K |
| shiny | yellowish shimmering to yellow-brown, iridescent | L |
| shiny | olive green to olive brown | M |
| high gloss | No color | N |
| arbitrary | Like B, C or D | P |
| matt | brown black to black | R |
| plain | brown black to black | S |
| shiny | brown black to black | T |
| all gloss levels | without chromating³ | U |
*Passivation is only possible for zinc or cadmium coatings. ²Applies only to zinc coatings ³Example of such a coating: A5U |
||
Notice: If the component hardness exceeds 320 HV or the tensile strength Rm exceeds 1,000 MPa, the manufacturing process must be checked using a hydrogen embrittlement detection test. In general, galvanic coating should not be applied at all in order to exclude the risk of hydrogen embrittlement fracture. If an electroplated coating is nevertheless to be applied, the parts must be annealed at approx. 200°C for approx. 6 hours at the latest 4 hours after the electroplating treatment. Subsequent heat treatment reduces the risk of hydrogen embrittlement, but complete elimination cannot be guaranteed. |
||
Sources:
|
||
Sonderschrauben Güldner GmbH & Co. KG collects and processes the personal data entered in the form in order to process the requested inquiry for you. Please note the marking of the mandatory fields on the forms. The legal basis for this processing of mandatory data is Art. 6 para. 1 lit. b GDPR, implementation of a pre-contractual measure. The processing of the data voluntarily provided by you is carried out on the basis of Art. 6 para. 1 lit. f GDPR. This permits processing that is necessary to safeguard our legitimate interests. Our legitimate interest is to have contact with you, our customers, to improve the quality of our advice and to be able to contact you more easily in the event of any queries. The data collected will only be stored by us for as long as is necessary to process your request and to contact you. It will then be deleted. Translated with DeepL.com (free version)
Additional data protection information, in particular on your rights to information, rectification, erasure, restriction of processing, objection and complaint, can be found in our privacy policy.